 |
This
section explains how to use the search language to search for objects. |
| |
The
search language offers almost all of the search functions available with
Edit > Search described in Selecting
Using the Search... Command. Searching using this command generates a
search query (expressed in the search language) displayed in the
Generated query box of the Search dialog box. The search
language can be used both in the power input box and in the Advanced
tab of the Search dialog box but also in macros. The search
query both searches for the elements and automatically selects them. |
| |
Any generated query
can be run via the power input box or in macros, whether transformat
or not.
However, the transformat query is the only usable query whatever the
session language, therefore any query you expect to run in different
session languages must be written in this format.
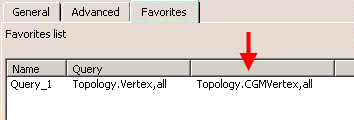
If you are not familiar with this format, you can display its
content and identify the syntax to be used prior to writing your
transformat query using a hidden column (you need to drag the column
separator next to the Query column to display it) in the Favorites
tab of the Search dialog box: |
| |
 |
| |
For instance,
CATDrwSearch.DrwText.Name=test,in means that you will search for
objects named "test" in the Drafting workbench using the "In <UI-Active
object>" scope. |
| |
This scenario deals with the following sections:
|
| |
To run a search via
the power input box, proceed as follows: |
 |
-
Enter the search string.
|
| |
-
Press Enter.
The searched objects are sent to the current command. If the
current command is the Select command, the objects are
selected.
The language to be used when entering your query is detailed
hereafter:
|
| |
Search Language: Syntax
|
| |
You can search for
objects using the same criteria as with Edit > Search. The
message catalog KeyboardInput.CATNls sets up the power input search syntax,
and search language shortcuts. The localized version of this message
catalog determines the exact syntax and shortcuts for each language.
|
| |
Using Operating
Signs
|
| |
The search
language uses the following separators (whose role you will discover in the
examples below):
- : and = (these separators are
interchangeable)
- != (different)
- <, <=, >, =>
|
| |
Searching by Name
|
| |
You can search for an object name.
This is particularly useful if you renamed objects using Edit >
Properties, or the Properties contextual command. The name
can also contain special characters. To search for an object by its name,
enter the following command:
name:object_name or
name=object_name
or a command using an abbreviation referred to as a "shortcut" as
follows:
n:object_name
where "object_name" is the name of the object.
You can also use the "*" character as a wildcard to replace any number
of characters. For example, the command:
name:wheel*
searches for all objects starting with the string "wheel".
The message catalog KeyboardInput.CATNls sets up unambiguous default
shortcuts. For example, there is no ambiguity between the shortcut c:
(used in the power input area to enter a command), and col:
(used for searches on color). In localized versions of the catalog, check
that there are no identical shortcuts for two different items.
If you want the search to be case sensitive, enter the following
command:
NAME:Wheel*
searches for all objects starting with the string "Wheel".
Note: the keyword used for queries that are not case sensitive is
always in lowercase whereas for case sensitive queries, the keyword is in
uppercase.
For languages that do not make any difference between uppercase and
lowercase characters, you can either add the string _CAP to
the keyword to specify that the query is case sensitive, or use the
Name_CAP transformat keyword.
|
| |
Searching by Name in
Graph
|
| |
You can search for
an object name. This search is different from searching by name since it
deals with the name as it is displayed in the specification tree. To
search for an object by its name as displayed in the specification tree,
enter the following command:
name in graph=object_name
If you want the search to be case sensitive, enter the following
command:
NAME IN GRAPH=object_name
|
| |
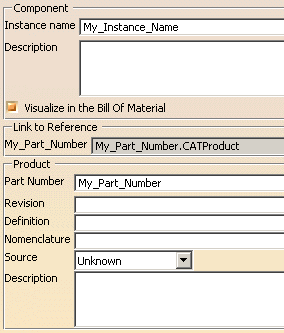
This name may be
customized and thus, may differ from the name you entered in the
Properties dialog box. For instance, suppose a part with named
"My_Part_Number"... |
| |
 |
| |
whose name is
displayed as follows in the specification tree: |
| |
 |
| |
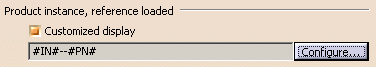
Let's suppose you
customize the display in
Tools >
Options > Infrastructure > Product Structure > Nodes Customization tab
by entering the following data: |
| |
 |
| |
The name displayed
in the specification tree now looks like this: |
| |
 |
| |
Entering:
name=*part*
gives no result since the search is based on the name displayed in the
Instance Name box. |
| |
But entering:
name in graph=*part*
finds the part. |
| |
Note that the tree
item size defined in the Tree Appearance tab is not taken into
account. |
| |
|
 |
| |
Searching by Type
|
| |
Use the Type
box in the Search dialog box to display a list of types (the
types are translated in each language). To search for an object by its
type, enter the following command:
type:type or type=type
or:
t:type
You can also search for types using the "."
(period) as follows:
For example, entering the command:
Part Design.Pad
searches for all objects of type Pad created using the Part Design
workbench.
The following syntax is also allowed:
workbench.type.attribute=
For example, entering:
Part Design.Pad.Color=Sea Green
searches for all objects of type Pad created using the Part Design
workbench, and of the color Sea Green.
You can omit the workbench name if the type exists only for this
workbench:
Part Design.Pad
and:
.Pad
are equivalent.
Similarly:
Part Design.Pad.Color=Sea Green
and:
type=Pad & Color=Sea Green
are also equivalent.
Here are some more examples using other operators described in
Using Operators:
workbench.type.name=point*
workbench.type.name!=point*
workbench.type.name:point*
and:
workbench.type.color='sea
green'
workbench.type.color!='sea green'
workbench.type.color:'sea green'
|
| |
|
 |
| |
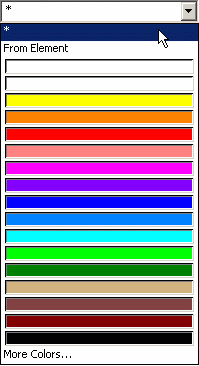
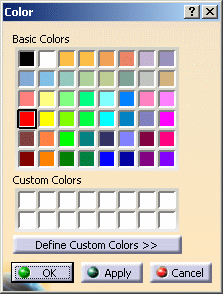
Searching by Color
|
| |
You assign colors to objects using
the Color list in the Graphic tab, when using
Edit > Properties or the Properties contextual command.
For a reminder about how to use this list, refer to
Displaying and Editing Graphic Properties.
To search for an object of a specific color, enter the following command:
color:color_name
or:
col:color_name
where "color_name" is the color of the object. |
| |
If the
name of the color contains a blank (which is the case with most of the
colors available), you can type the full name as follows: color:Sandy
Brown
You can also surround the blank or the color name with a single quote
(by default) like this:
color:Sandy' 'Brown
or like this:
color:'Sandy Brown'
You can also search for colors using their RGB
values. For example:
color:'(211,178,125)'
|
 |
|
| |
 |
| |
|
| |
 |
| |
|
| |
|
 |
| |
Searching by Product Properties
|
| |
You assign properties to products (and parts in products) by right-clicking
an element in the specification tree and selecting
Properties,
clicking the Product tab in the Properties dialog
box, and setting the properties in the Product frame.
The properties you can search for (the same as those
you assigned to the element) are:
- Part Number
- Revision
- Definition
- Nomenclature
- Product Description
- Component Description.
For example, the search queries:
Product Description:completed
Product' 'Description:completed
'Product Description':completed
'Product Description'=completed
search for all elements whose Product Description is the text
"completed".
The property name is case sensitive. |
| |
Searching for Objects Belonging to a Layer
|
| |
To search for an
object belonging to a specific layer (as seen in the Graphic
Properties toolbar), enter the following command: l:layer_number
or l=layer_number
or
layer:layer_number or
layer=layer_number
where "layer_number" is the number of the layer. |
| |
Searching for Objects Belonging to a Selection Set
|
| |
To search for an
object belonging to a selection set, enter the following command:
s:selection_set_name
or
set:selection_set_name
where "selection_set_name" is the name of the selection set.
If you want the search to be case sensitive, enter the following
command:
SET=selection_set_name
The strings "name", "type", "color" and "set" are appropriate for the
English language only. The message catalog KeyboardInput.CATNls determines
the exact syntax for your language.
|
| |
|
 |
| |
Searching for Visible or Hidden
Elements
|
| |
You can search for
visible, invisible, shown elements, or elements hidden in the No Show space
using the following syntax:
visibility:visible
vis:visible
and:
visibility:hidden
vis:hidden
|
| |
Searching
for Line Thickness or Linetype
|
| |
You can also
search for objects with a specific line thickness or linetype (as seen in
the Graphic Properties toolbar) like this:
weight:
w:
or:
dashed:
d:
When searching for lines with a specific weight, you can specify the
weight index like this:
weight:6,all
to search for all lines which are 2.0000 mm thick.
|
 |
Searching by Symbol
|
| |
|
| |
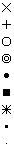 |
Cross |
| Plus |
| Circle |
| Double Circle |
| Dot |
| Full Square |
| Star |
| Small Full Square |
| Small Dot |
|
| |
Searching Using Favorites
|
| |
You can search for
objects using your favorite queries defined via the
Favorites tab in the Search dialog
box. To do so:
favorite=favorite_query_name
or favorite:favorite_query_name
but you can also enter:
f=favorite_query_name
or f:favorite_query_name
where "favorite_query_name" is the name of the favorite query. Note that
the language used in favorite queries is case sensitive.
When you press Enter, the search results are selected in the
specification tree. |
| |
You can use any of
the special characters such as !. For example, let's
use the query defined in Searching Using the
Favorites Mode. This query searches for any element named "My Sketch".
Now, suppose you want your search to select all elements whose names are
other than "My Sketch", you just have to type:
favorite!=Query_1
or
f!=Query_1
In that case, the search scope is not modified. |
| |
To modify the
search scope, indicate the new scope after the favorite query name in the
power input box:
favorite=Query_1, from
searches for any element named "My Sketch"
From Search to bottom
and not Everywhere as originally defined in Query_1. The new
scope supersedes the previous one.
|
| |
|
 |
 |
Searching Using Predefined
Favorites
|
| |
|
| |
Search with no selection required
|
| |
|
| |
| |
Shortcut for |
Searches for |
* |
t:*,all |
all objects
everywhere (i.e. in the whole specification tree from top to bottom) |
*PLN |
.Plane,all |
all planes
everywhere |
*SUR |
.Surface-.Plane,all |
all surfaces
(except planes) everywhere |
*FAC |
.Face,all |
all
topological faces everywhere |
*VOL |
.Volume,all |
all volumes
everywhere |
*LN |
.Line-.Sketcher.Line,all |
all lines
(except sketcher's) everywhere |
*PT |
.Point-.Sketcher.Point,all |
all points
(except sketcher's) everywhere |
*CRV |
.Curve-.Line-.Sketcher.Curve,all |
all curves
(except sketcher's and lines) everywhere |
*SKT |
.Sketch,all |
all sketches
everywhere |
*AXS |
.Axis
System+.AbsoluteAxis,all |
all axis
systems (including sketcher's) everywhere |
*FTA |
.Functional
Tolerancing & Annotation Element |
all
Functional Tolerancing & Annotation elements everywhere |
|
| |
|
 |
|
| |
Search with selection
|
| |
|
| |
| |
Searches for |
*COL |
all objects
with the same color as the selected object |
*LAY |
all objects
included in the same layer as the selected object |
*LNW |
all lines
with the same thickness as the selected object |
*LNT |
all lines
with the same linetype as the selected object |
*PTT |
all points
with the same point type as the selected object |
*PRT |
all objects
included included in the same part as the selected object |
*PBD |
all objects
included included in the same part body (or hybrid body) as the
selected object |
*GST |
all objects
included included in the same geometrical set (named "open body" before
V5R13) as the selected object |
*OGS |
all objects
included included in the same ordered geometrical set (named "shape
body" before V5R13) as the selected object |
|
| |
|
| |
 |
| |
|
| |
|
 |
| |
Search with
arguments
|
| |
|
| |
| |
Shortcut for |
Searches for |
*COL<xxx> |
Color=xxx,all |
all elements
with the color xxx everywhere, where xxx is the RGB code
(e.g. *COL'(0,0,255)' when searching for the "blue" color)
or the color name (e.g. *COLblue) or the color index (e.g.
*COL45) |
*SST<xxx> |
Set=xxx,all |
all objects
in the selection set xxx everywhere (where xxx is the
name of the set, e.g. *SST'Set1' or SSTSet1) |
*LAY<n> |
Layer=n,all |
all objects
in the layer n everywhere (where n is the layer number,
e.g. *LAY2) |
*LNW<n> |
.Line &
Weight=n,all |
all lines
drawn with the thickness index n, as displayed in the
Weight list of the Search dialog box, everywhere
(e.g. *LNW3 to search for a 0.7000 mm line:
 ) ) |
*LNT<n> |
.Line &
Dashed=n,all |
all lines
drawn with the dashed index n, as displayed in the Dashed
list of the Search dialog box, everywhere (e.g. *LNT2
to search for a "Dotted" line:
 ) ) |
*PTT<n> |
.Point &
Symbol=n,all |
all points
drawn with the symbol n, as displayed in the Symbol
list of the Search dialog box, everywhere (e.g. *PTT8
to search for the eighth symbol in the
list, from top to bottom:
 ) ) |
|
| |
|
 |
|
| |
|
 |
| |
Using Special
Characters
|
| |
Characters
& + - ( ) play a
special role in the search syntax:To be
interpreted literally in names, those characters or text strings containing
those characters must be surrounded by the character
'(apostrophe by default).
For example:
n:*')'
searches for all names
ending with )
n:*'&'
searches for all names
containing &
n:*'(1)'
searches for all names
ending with (1).
The following line in the KeyboardInput.CATNls resource file :
Quote = " ' ";
specifies the default character for surrounding strings. |
| |
The
character * is always interpreted as a wild card except if surrounded by
two characters '. For example:
n:*''*''
searches for all names
ending with *
n:*''*''*
searches for all
names containing *
n:*'&'''*''*
searches for all
names containing &*
n:'*)'
searches for all names
ending with ). This is identical to n:*')' |
| |
The
character ' must be doubled twice to be interpreted literally.
For example:
n:*''''*
searches for all names
containing a '
n:P''''*
searches for all names
beginning with P'
n:P''''''''*
searches for all
names beginning with P''
n:P''''''''''''*
searches for
all names beginning with P'''
n:P''''''''''''''''*
searches
for all names beginning with P''''.
|
| |
Using Operators
|
| |
The supported
operators are: &, +, and - (for AND,
OR and EXCEPT respectively) and ( ).
Blanks are not considered as separators. They
may be surrounded by ', but this is not mandatory. |
| |
Combining standard queries
|
| |
The following
examples: name:*wheel'&'door&type:Part
name:*wheel'&'door & type:Part
name:*'wheel&door' & type:Part
name:*'wheel&door'& type:Part
name:*wheel'&'door &type:Part
all search for parts whose names end with "wheel&door".
The command:
name:wheel1 + name:wheel2
searches for objects named "wheel1" and objects named "wheel2". |
 |
Combining predefined favorite queries, favorite queries and standard
queries
|
| |
|
 |
|
| |
Combining predefined favorite queries
|
| |
|
| |
Combining predefined favorite queries and favorite queries
|
| |
|
| |
Combining predefined favorite queries and standard queries
|
| |
|
| |
Combining predefined favorite queries, favorite queries and standard
queries
|
| |
|
| |
|
 |
| |
Priority
|
| |
There is no priority among
operators, but there is a priority in their order of appearance (from left
to right). For example, the query:
type:Part* & name:toto + type:Hole & Color:Black
is interpreted as:
type:Part* & (name:toto +
(type:Hole & Color:Black) )
and thus searches
for elements of type "Part" among the objects in the document that are
"black holes" or named "toto".
To avoid ambiguity,
use parentheses like this:
type:Part* & (name:toto + (type:Hole & Color:Black) )
to obtain the same result.
|
| |
Using Search
Scopes
|
 |
You can use the same search scopes
(except In List) as with Edit > Search, by using
the context aliases all, in, from,
sel and :
all: searches the whole specification tree from top to
bottom, to find objects created using all workbenches. in: locates the appropriate elements in the active
object and in the workbench you are currently using from: searches the elements in the active object to the
bottom of the tree. For example, in a Part document, both parts and
sketches are searched. sel: if you already selected objects before selecting
Edit > Search, this option searches from the selected objects
to the bottom of the tree.
The default is in. Scope aliases must always be placed at
the end of the search string, and after the separator "," like this:
type:Hole, all
The separator is the comma (",") for the English, Japanese, Korean and
simplified Chinese environments, and the semi-colon (";") for all other
supported environments. |
 |
Using a Default Prefix
|
| |
|
| |
|
 |
Using a Default Search Scope
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
 |
|
 |
![]()







